2022 Threat Roundup

2022 Threat Roundup – The Emergence of Mixed IT/IoT Threats
In 2022, cyberattacks grew in intensity, sophistication and frequency. The adoption of new connected devices by organizations in 2023 is likely to pose even greater challenges. To help organizations of all sizes prepare, Forescout’s Vedere Labs has analyzed data gathered in 2022 about cyberattacks, exploits and malware and shared insights via our 2022 Threat Roundup.

100 Million
Attacks Jul. – Dec. 2022

10 Attacks
Per Second

7000
Exploits

1000
Unique Malware Samples
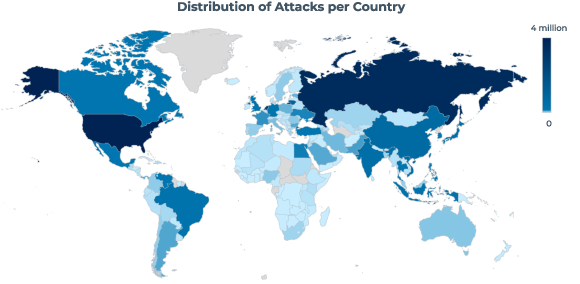
Attacks come from everywhere…
- Attacks originated from 191 countries and territories
- Top 10 countries account for 73% of malicious traffic
- 75% of exploits originated from U.S. and China
- 81% of attacks launched from legitimate hosting/cloud providers
Top Executed Command Categories
Remote management services are the top target…
- 43% of attacks target remote management protocols (RDP, VNC, SSH, Telnet)
- 26% target web protocols (HTTP and HTTP/S) for scanning or vulnerability exploitation attempts
- Mainly exploited using brute forcing with well-known or weak credentials
Top Exploited Software Type
MODBUS Enumeration
...and critical infrastructure is a constant target
Attackers constantly probe multiple OT devices and protocols for malicious reconnaissance, including scans for:
- OPC-UA, S7, Ethernet/IP, Modbus – used in industrial automation to exchange input/output data or manage devices such as PLCs
- Fox – used in building automation to control devices (lighting, HVAC, access control)
- DNP3, IEC-104, MMS and IEEE-C37.118 Synchrophasor – used in energy and water sectors
Distribution of Malware Hashes per Family
Strategic Recommendations: How Forescout Can Help
To protect your environment from mixed IT/IoT cyber threats, focus on these three key pillars:
- Risk and exposure management. Identify, quantify and prioritize cybersecurity risk, starting by discovering and assessing every connected asset for real-time awareness of your attack surface.
- Network security. Continuously monitor all connected assets to govern network access, using real-time traffic visibility to manage segmentation and dynamic control policies to mitigate and remediate risk.
- Threat detection and response. Detect, investigate and respond to true threats and incidents using threat detection and response capabilities to collect telemetry and logs, correlate attack signals, generate high-fidelity detections and enable automated responses.
For more detailed recommendations, read the report.