CYBERSECURITY A-Z
According to the United States’ Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA), ransomware is an ever-evolving form of cybercriminal activity using malware designed to encrypt files on a device, rendering any files and the systems that rely on them unusable. Malicious actors then demand a ransom (often in cryptocurrency like Bitcoin) in exchange for decryption.[i]
In another form, hackers uses malware to gain control of a computer, operating system, or network, often shutting down part or all of it to demonstrate control. They then demand a ransom in exchange for returning control to the compromised organization.
Regardless of the method used to gain control of a computer, network, and/or data, malicious actors typically use ransomware to extort companies, organizations, or individuals. They most frequently threaten to either maintain their hold over the victim organization’s network infrastructure or sell/leak exfiltrated data if a ransom is not paid.
Based on the latest data from the first six months of 2025, Forescout Research – Vedere Labs reports:
- A 36% year over year increase
- Total: 3,649 attacks
- 608 attacks/month, 20/day
- The U.S. is the most targeted country at 53%
- Top 5 industries targeted: Services, manufacturing, technology, retail, and healthcare
Today, this malware is often sold on the Darkweb as a packaged service for bad actors as ‘Ransomware as a Service’ or RaaS. Vedere Labs tracks ransomware actors in our Adversary Engagement Environment — a honeypot that captures many different kinds of attacks in the wild to study the techniques of cybercriminals.
Many of the RaaS services are managed by threat actor groups which Vedere Labs also tracks. Key developments: Cl0p became the most active group, overtaking LockBit, which dropped to 19th position following a major law enforcement operation in February 2024 and a leak of their affiliate panel data in 2025. Only four groups from last year’s top 10 remained in the top tier: Akira, RansomHub, Play, and Medusa. Overall, the ransomware landscape continues to fragment and expand although growth is slowing. The top 10 groups accounted for 59% of attacks in 2024H1 and 60% in 2025H1 while the number of active groups increased from 82 to 89, an 8.5% increase.
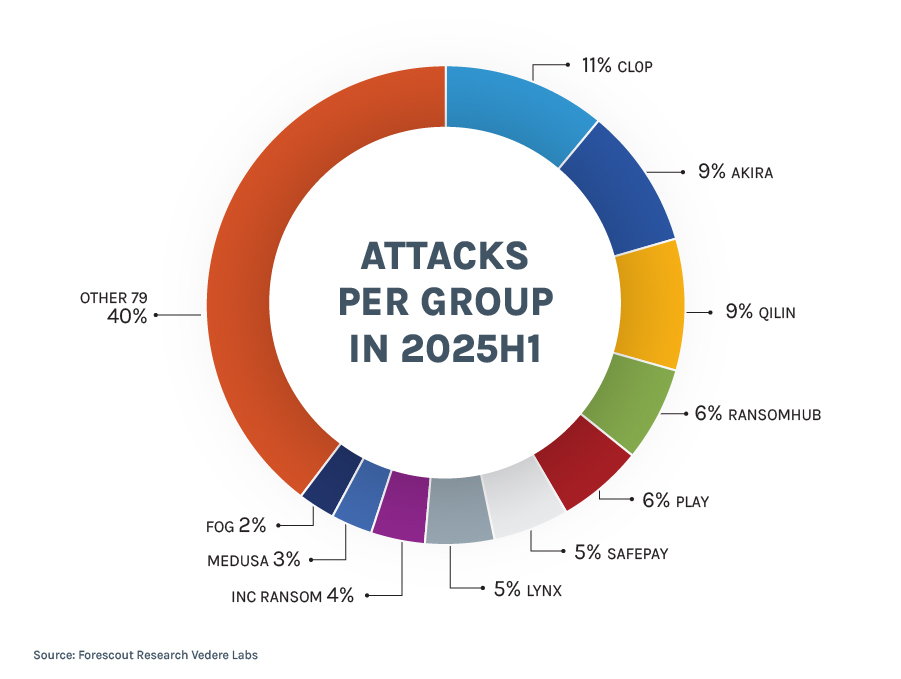
The Adverse Impact of Ransomware Attacks on Organizations and People
Ransomware incidents ― and their associated data breaches ― can severely impact business processes by leaving organizations unable to operate critical infrastructure, run network-connected devices, and/or access necessary data to deliver mission-critical services. The impact across industries and populations can range widely, from inconveniencing customers, to threatening the health and well-being of people, as demonstrated by these recent incidents:
Healthcare
In May 2024, attackers infiltrated Tennessee-based HCA Healthcare, the largest health system in the United States, stealing protected electronic health information of 191 million people. Not only did the parent company (Change Healthcare) pay a $22 million ransom, but patients of multiple affiliated healthcare organizations found themselves locked out of their data and unable to obtain their medications without having to pay out of pocket.[ii] It took months for Change to restore all systems and the company had to testify at least twice before Congress.
Municipal Government
In June 2024, The city of Cleveland, Ohio shut down City Hall because of a disruptive attack. Since city leaders decided to not pay the demanded ransom, City Hall remained closed for eleven days. During that time, many Cleveland residents were affected and unable to submit payments, secure building permits, or progress housing applications.[iii]
Colonial Pipeline Company
In May 2021, the hacker group Darkside gained access to Colonial’s network via an employee’s stolen VPN password. The password had been compromised in a previous data breach and reused to access the company’s network. The breach posed a major threat, as Colonial Pipeline is one of the longest oil pipelines in the U.S. and supplies approximately 45 percent of the oil consumed on the East Coast for both fuel and heating purposes. In the end, the hackers were seeking money only, and having stolen 100 gigabytes of data within two hours, threatened to release it if not paid the ransom of 75 bitcoins.[iv]
The economic and reputational impacts of operational interruptions and data extortion have proven challenging and costly for organizations of all sizes, often throughout the initial disruption and during response and recovery. Extortion payments to criminal groups hit record highs in 2024. In the U.S. alone, victims paid $460 million to cyber criminals. One Fortune 50 company even paid a $75 million ransom to the Dark Angels criminal group. On average, criminals demanded $2.73 million per successful infiltration.[v]
Healthcare – At Special Risk of Cyber Attacks
The below chart from Statista shows a typical three-month period during 2024, and as usual, Healthcare bore the largest brunt of ransomware attacks among all industries in the United States.
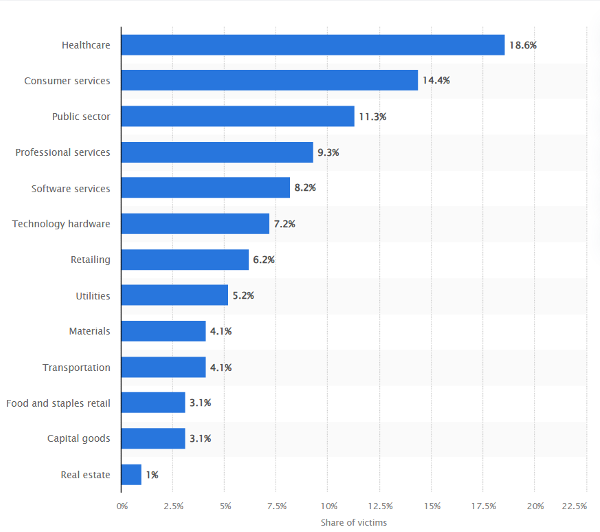
Industries Most Frequently Impacted by Ransomware in the United States in 2024
What makes Healthcare such an attractive target?
Healthcare has become a prominent target sector for ransomware groups because they know that organizations are under heavy pressure to overcome service and patient care disruptions quickly. A second reason is that healthcare networks are often highly complex, making them more difficult to defend than networks in some other industries. Not only must the enterprise network be protected, but so too must the networks of affiliates and partners. Then there are the thousands of medical devices, from infusion pumps to MRI machines, that connect to the network. The end result is a massive attack surface, and cyber criminals only need to find a single exploitable vulnerability in it to succeed.
In our recent report on the risks of IoMT devices, we revealed that around 50% of devices in healthcare networks are unmanaged. That introduces risks, such as lack of visibility and limited possibilities for threat detection.
One must also keep in mind that Healthcare is a highly regulated industry. Organizations that run afoul of the patient privacy protections and general security prescribed by the HIPAA Security Rule face fines, penalties, and other governmental actions.
Finally, there is the pressure to pay and the practice of paying out large sums. According to a recent report from Microsoft:
- Healthcare organizations that admit to paying ransom demands have paid $4.4 million, on average.
- Such attacks cost healthcare organizations $900,000 per day on downtime alone.
- These attacks affect both the targeted organizations and other neighboring hospitals that must care for the patients who cannot be treated in the targeted hospitals. This has led to an increase of 35% in emergency arrivals and 15% in overall patient volume when such incidents occur.
All of this is not to say that other industries are much safer than Healthcare. As we noted above, attacks happen quite often in multiple industries, and they present special dangers to the public in critical infrastructure industries like Energy, Water, Transportation, and Defense.
How Should Organizations Respond to Threats?
In the face of an increasing volume and sophistication level of attack tactics, including phishing and the use of AI to fool users into giving criminals network access, organizations should take the following four steps to address vulnerabilities in their network:
- Proactively and holistically manage their security posture. Doing so makes it possible to address vulnerability discovery and mitigation, misconfiguration detection and exposure management.
- Adopt and effectively use encryption. This helps defend against and mitigate the consequences of today’s attacks, and serves as a legal safeguard.
- Understand and enumerate digital assets and backups. It’s essential to have a view of both managed and unmanaged/unknown assets, including data, applications, and systems (IT, OT, IoT, IoMT). And it’s crucial to have a data backup plan in the event of it being taken hostage.
- Measure exposure to potential threats. Which services are running? Is the asset exposed to the internet? Can the asset be directly managed? Is the asset currently compliant? What are the consequences to the business if an asset is degraded, compromised or unavailable?
By identifying the greatest risk (e.g., assets with higher exposure facing a more critical threat), organizations’ risk management teams can prioritize their efforts most effectively.
How Forescout Can Help Prevent and Respond to Attacks
When you automate cybersecurity and policy enforcement with the Forescout 4D Platform™, you optimize security across all your electronic infrastructure – networks, devices, software, and systems.
The Forescout 4D Platform™ continuously identifies, helps protect, and ensures the compliance of all managed and unmanaged cyber assets – IT, IoT, IoMT and OT – without business disruption. It delivers comprehensive capabilities for network security, risk and exposure management, and extended detection and response. With seamless context sharing and workflow orchestration via ecosystem partners, it enables you to more effectively manage cyber risk and mitigate threats.
Key components of the platform include:
- Asset Discovery: This involves pinpointing all the digital assets within an organization’s network, including devices, applications, and systems. A comprehensive inventory is necessary to manage the attack surface effectively.
- Vulnerability Assessment: Once the assets are identified, a thorough vulnerability assessment is conducted to identify weaknesses and potential entry points for cyber attackers. This assessment aids in prioritizing remediation efforts and reducing the overall risk.
- Continuous Monitoring: The attack surface constantly evolves due to many factors, such as software updates, new devices, or changes in network configurations. Continuous monitoring ensures prompt identification and addressing of any changes to the attack surface.
- Threat Intelligence: To stay ahead of cyber threats, organizations need access to current information about emerging vulnerabilities and attack techniques, including ransomware detection. Integrating threat intelligence helps organizations proactively defend against potential attacks.
Some major benefits of Platform 4D include:
- Comprehensive Asset Visibility and Management: Organizations gain a complete view of their cyber assets, including on-premises, cloud-based, and remote systems. This visibility helps to better understand and manage the attack surface, leading to a more robust security posture. By automating asset inventory and streamlining management, Forescout simplifies the process of discovering and fixing security gaps.
- Enhanced Security Hygiene and Threat Prioritization: Forescout offers valuable insights into an organization’s security controls, overall security posture, and exposure of assets. This enables security teams to address vulnerabilities and misconfigurations, improving overall security hygiene proactively. By evaluating asset criticality and vulnerability severity, Forescout helps prioritize threats, ensuring that the most critical risks are dealt with first, thus minimizing the potential impact of cyber-attacks.
- Real-time Monitoring, Remediation, and Integration: Forescout continuously monitors an organization’s attack surface, detecting changes and new vulnerabilities in real time to swiftly identify and address threats. It integrates with existing security infrastructure, such as endpoint protection solutions, to facilitate data sharing and coordinated response across the security ecosystem.
- Improved Compliance, Cyber-Resilience, and Productivity: Forescout promotes data-driven decision-making, assisting in regulatory compliance and bolstering cyber-resilience by identifying and mitigating vulnerabilities before they are exploited. Forescout’s automation of asset list maintenance and streamlining of management processes enables security teams to prioritize strategic tasks, thereby enhancing overall productivity.
Experience the power of the Forescout 4D Platform™ – schedule your demo today and protect your expanding attack surface from new and evolving ransomware threats.
[i] CISA. Ransomware 101. Accessed May 1, 2025 from the following source: https://www.cisa.gov/stopransomware/ransomware-101
[ii] Steve Alder. The HIPAA Journal (2025). The Biggest Healthcare Data Breaches of 2024, January 7, 2025. Accessed March 10, 2025 from the following source: https://www.hipaajournal.com/biggest-healthcare-data-breaches-2024/
[iii] Arielle Waldman (2024). 10 of the biggest ransomware attacks in 2024, December 10, 2024, TechTarget. Accessed May 1, 2025 from the following source: https://www.techtarget.com/searchsecurity/news/366617564/10-of-the-biggest-ransomware-attacks-in-2024
[iv] CDW (2022). Ransomware Attacks in the Energy Industry, May 5, 2022, CDW. Accessed May 1, 2025 from the following source: https://www.cdw.com/content/cdw/en/articles/security/ransomware-attacks-energy-industry.html
[v] Mike Elgan (2024). Roundup: The top ransomware stories of 2024, December 5, 2024, IBM. Accessed May 1, 2025 from the following source: https://www.ibm.com/think/insights/roundup-the-top-ransomware-stories-of-2024